

He observed that the luminescent glow increased dramatically as the pressure within the tube continued to decrease. A student of Plucker's, Hittorf further improved the method for creating a vacuum within glass tubes of his own design. The next scientist to conduct important research using vacuum tubes was Johann Hittorf ((1824-1914) in 1869. The discovery indicated that the stream crossing the vacuum was composed of particles rather than rays. The glow could be moved by a powerful magnet. Second, he found that the glow responded to a magnetic field. The glow was much brighter than any achieved in previous experiments. First, he was able to produce a bright stream-like glow between the electrodes. Using the improved vacuum tube, Plucker made some startling discoveries. The new vacuum tubes were very popular, and became known as "Geissler's tubes". He constructed a hand-crank mercury pump that could remove most of the air from a tube. Sometime around 1855, Plucker convinced Geissler to design an apparatus for evacuating (completely emptying) a glass tube. Geissler was a skilled glassworker, employed by the University of Bonn ( Germany) as a maker of scientific instruments. The German team of Heinrich Geissler (1815-1879) and Julius Plucker (1801-1868) pioneered the study of cathode-ray tubes. Faraday was not able to explore this effect completely because technology was not advanced enough to produce a high vacuum within the tube. It was English physician and chemist Michael Faraday (1791-1867) who noticed that as the amount of air in the tube decreased, a faint glow between the electrodes could be seen. When most of the air was evacuated from the tube, an electrical charge could be seen jumping across the gap between the two electrodes. Early ExperimentationĮarly experiments to solve the riddle of electricity often included the use of anode-cathode tubes (glass tubes that contained an anode at one end and a cathode at the other). Great scientists like Henri Becquerel (1820-1891 French chemist and an authority on luminescent, or light caused by radiant energy, phenomena), Marie Curie (1867-1934 Polish-born French physicist who worked extensively with radium) and Thomas Young (1773-1829 English physician and physicist) led the way.

Phenomena that had never before been truly understood, such as light, heat, and electricity, were systematically explored. Also with sensors and data logger in Sk087 the accelerating voltage can be automatically varied and plate current measured & displayed graphically on PC.In the mid to late 1800s, the world experienced a scientific revolution.
#HERTZ CATHODE RAY EXPERIMENT MANUAL#
The experiment can be performed in manual mode where the accelerating voltage and the plate braking voltage can be manually controlled in SK090. In the present Franck-Hertz experiment with neon gas, the absorbed energy by neon atoms is released through photons having red-orange wavelength, which can be visually observed in band formations. These dips in current is observed at approximately fixed intervals of accelerating potential which demonstrate the presence of discreet or quantum energy levels in the Bohr’s model of atom. Thus fewer electrons reach the anode plate and there is a dip in the plate current. As accelerating potential is increased the gas atoms absorb energy as they are excited due to in-elastic collision by the energized electrons. At low accelerating potential, the electrons gain kinetic energy and reach the anode plate with purely elastic collisions with the gas atoms.

The mesh grids provide the accelerating potential to electrons and the anode is held at slightly negative potential to provide braking.
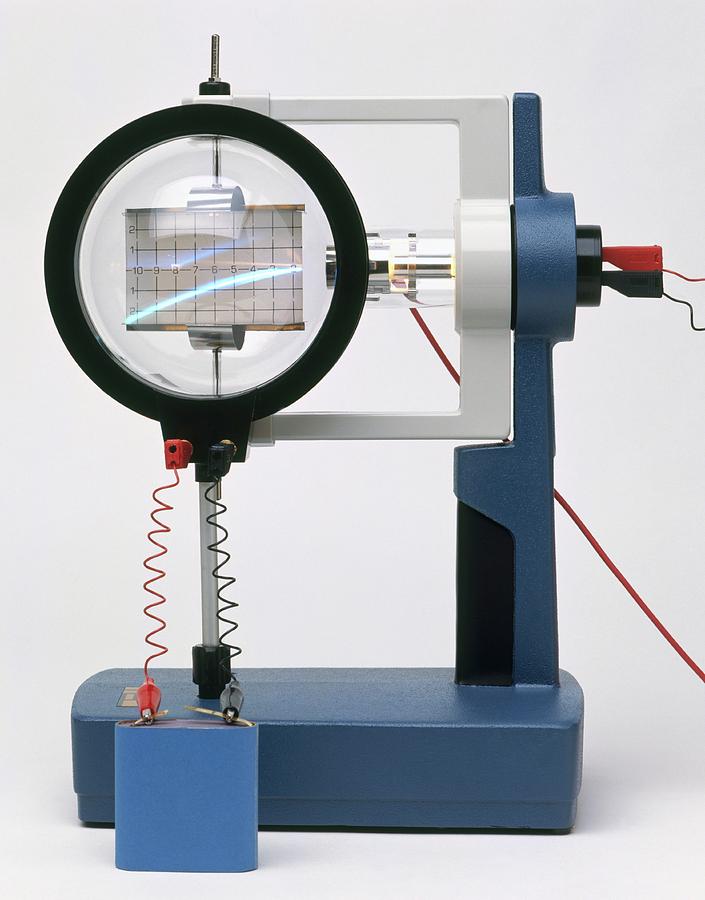
The Franck-hertz tube consists of an electron-emitting cathode, two mesh grids for accelerating electrons and an anode plate for collecting electrons. Frank Hertz Apparatus (SK090- consisting of CD133 & CD152) can be operated in stand alone mode.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
