
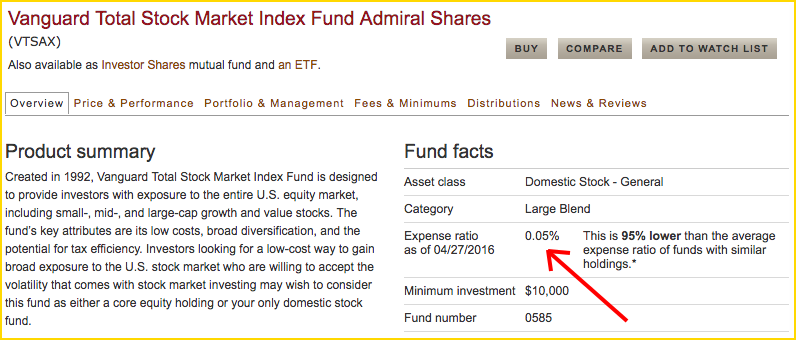
Part 11: The EBITDA measurement of profitability Part 3: Working capital to gross revenues You can read the other articles in this series: Operating-Expense Ratio = (Total operating expense not including interest – depreciation) / gross income The following equation(s) will determine your Operating-Expense Ratio: When you add the following financial ratios they should total 100%: A number less than 60% means the business or farm is on strong footing while anything higher than 80% means the farm or business is going to be more easily vulnerable to changes in markets. The lower the percentages the better position a farm or business is. The Operating-Expense ratio shows the proportion of income that is being used to cover operating expenses not including the principal and interest of loans.

Operating-Expense ratio is measured as a percentage, the lower the percentage the better the situation is for the business or farm. effects the gross income of the business. Looking at the financial efficiency of a business or farm assists the owner(s) in determining how the various aspects of the business such as production, financing, marketing, etc. Financial efficiency refers to how effectively a business or farm is able to generate income. Operating-Expense ratio is a measurement of financial efficiency and is determined based on information derived from a business or farm operation’s financial statements specifically using the financials that determine gross farm income.
#NET EXPENSE RATIO SERIES#
This series of articles will look at 21 commonly used ratios and indicators. Multiple ratios and indicators must be used along with other information to determine the total and overall health of a farming operation and business. You cannot look at a single ratio and determine the overall health of a business or farming operation. There is a minimum of 21 different ratios and indicators that can be looked at by many financial institutions. Therefore, for true comparison, the investor must adjust the expense ratio for the interest and excess returns then then compare the expense ratio for different funds.Financial ratios & indicators can assist in determining the health of a business. This is because even though interest is an actual expense paid by the fund, it also creates excess returns. Since many leveraged funds include interest expense in the total expense ratio, this makes it difficult for investors to compare them with non-leveraged funds. However, the payments to preferred shareholders are not included in the expense calculation, even though it is similar to interest payments to bond holders. It is important to note that other than borrowing money and issuing debt securities, a CEF can also issue preferred shares to create leverage. The expense ratio of a CEF generally ranges from 0.25% to 2% or higher. The total expense is listed as a percentage of the total fund assets.
The expense ratio does not include sales fees and other redemption charges that are levied at the time of sale/purchase of fund shares. These expenses are towards the annual operating expenses of the fund and include fund management fee, distribution/services fee and other administrative expenses.Īs per Investment Company Act of 1940, the debt-leveraged CEFs must include the interest expense on the debt in their expense ratio.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
